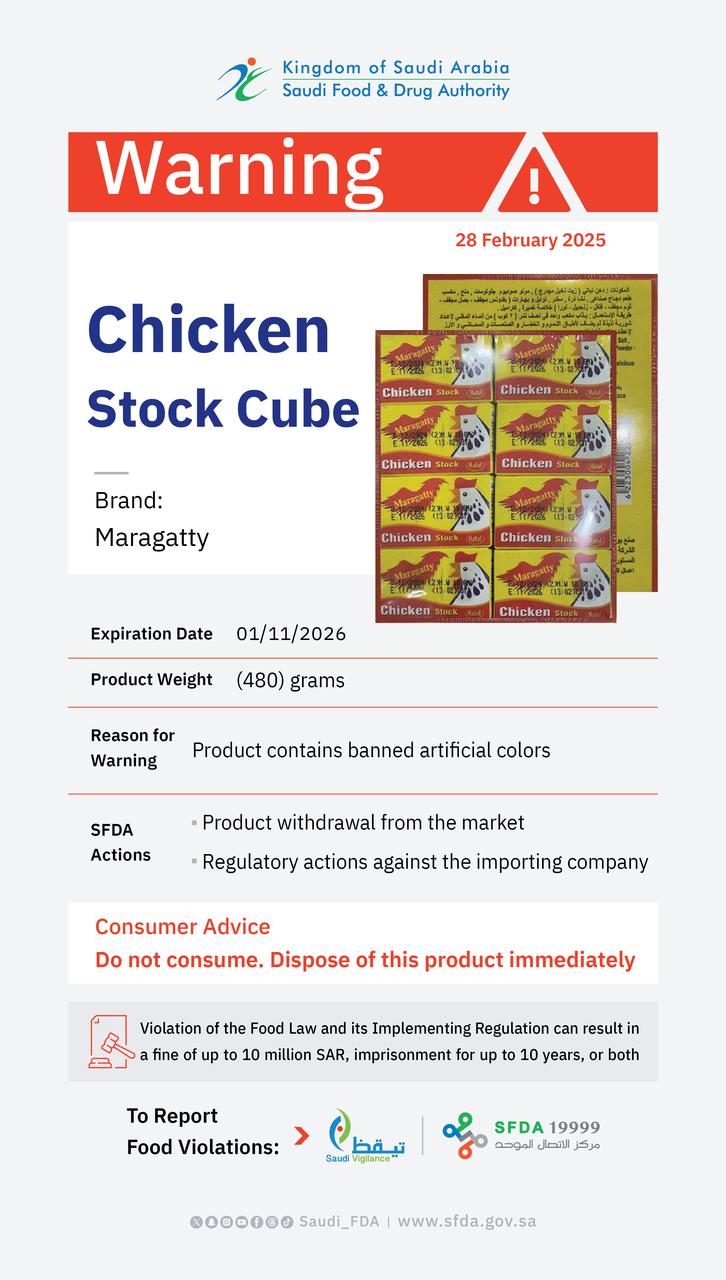
New Boxed Warning on severe liver injury with propylthiouracil
2010-05-05
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) the American counterpart to the Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) has added a Boxed Warning to the label for propylthiouracil, a drug used to treat hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), to include information about reports of severe liver injury and acute liver failure, some of which have been fatal, in adult and pediatric patients using this medication.
The new warning also states that for patients being started on treatment for hyperthyroidism it may be appropriate to reserve use of propylthiouracil for those who cannot tolerate other treatments such as methimazole, radioactive iodine or surgery. In addition, due to the occurrence of birth defects that have been observed with the use of methimazole during the first trimester of pregnancy (see Data Summary), propylthiouracil may be the treatment of choice during and just before the first trimester of pregnancy.
Propylthiouracil has been shown to be effective in reducing thyroid hormone levels and decreasing symptoms associated with hyperthyroidism. However, to help patients understand the known benefits and potential risks of this medication, as part of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), FDA is requiring that a Medication Guide be given to every patient filling a prescription for propylthiouracil.
The recommendations in the Boxed Warning and the requirement of a Medication Guide are based on FDA's review of post-marketing safety reports of propylthiouracil (see Data Summary) as well as meetings with the American Thyroid Association, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the pediatric endocrine clinical community.
Healthcare professionals should be aware of this new safety information in the drug label and follow the recommendations outlined above. Patients should carefully read the Medication Guide each time they get their prescription so they are aware of the risks and benefits of this medication.
Additional Information for Patients
Be aware that severe liver injury has occurred in patients taking propylthiouracil.
Read the Medication Guide when picking up a prescription for propylthiouracil. It will help you understand the potential risks and benefits of this medication.
Contact your healthcare professional if you have fever, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, tiredness, itchiness, dark colored urine, or yellowing of your skin or eyes while taking propylthiouracil.
Propylthiouracil may be the treatment of choice during and just before the 1st trimester of pregnancy (weeks 1-12). Talk to your healthcare professional if you are pregnant (or plan to become pregnant) and are taking a medication to treat hyperthyroidism.
Tell your healthcare professional about any medication you are taking or medical conditions you may have before taking propylthiouracil.
Do not stop taking propylthiouracil unless told to do so by your healthcare professional.
Additional Information for Healthcare Professionals
Be aware that severe liver injury and acute liver failure, including fatal cases, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients taking propylthiouracil.
When initiating hyperthyroid treatment, propylthiouracil should be reserved for patients who cannot tolerate methimazole or for patients for whom radioactive iodine therapy or surgery is not appropriate treatment.
Propylthiouracil may be the treatment of choice when an antithyroid drug is needed during and just prior to the 1st trimester of pregnancy. Fetal abnormalities have been seen with methimazole use during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Propylthiouracil is not recommended for use in pediatric patients, except in rare instances in which other alternative treatments are not appropriate.
Encourage patients to read the Medication Guide when picking up their prescription for propylthiouracil.
Review the newly revised label for complete information on the use of propylthiouracil.
Report Adverse Drug Reactions to the Saudi FDA
The SFDA urges both healthcare professionals and patients to report side effects from the use of botulinum toxin products to the SFDA either online, by regular mail or by fax, using the following contact information :
National Pharmacovigilance Center (NPC)
Saudi Food and Drug Authority-Drug sector
3292 Northern Ring Road
Al Nafal District
Riyadh 13312 – 6288
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Email :
Website:
Resorce: